-
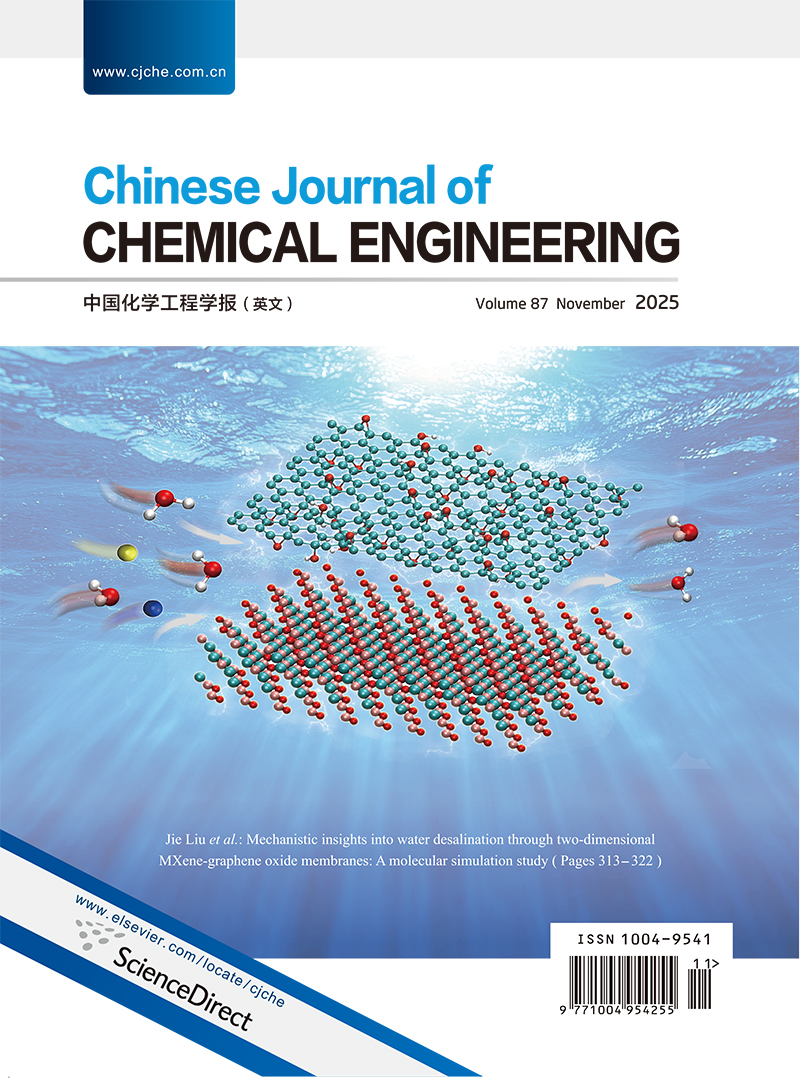
Schematic illustration of water desalination through two-dimensional MXene/graphene oxide (GO) composite membranes. The ordered water structure induced by MXene facilitates fast water transport, while the MXene/GO composite membranes with narrow interlayer spacing efficiently reject salt ions. The molecular dynamics simulations reveal the structural and functional synergy between MXene and GO, providing mechanistic insights into the design of high-performance 2D membranes for desalination. (See Jie Liu et al., Pages 313-322)
-
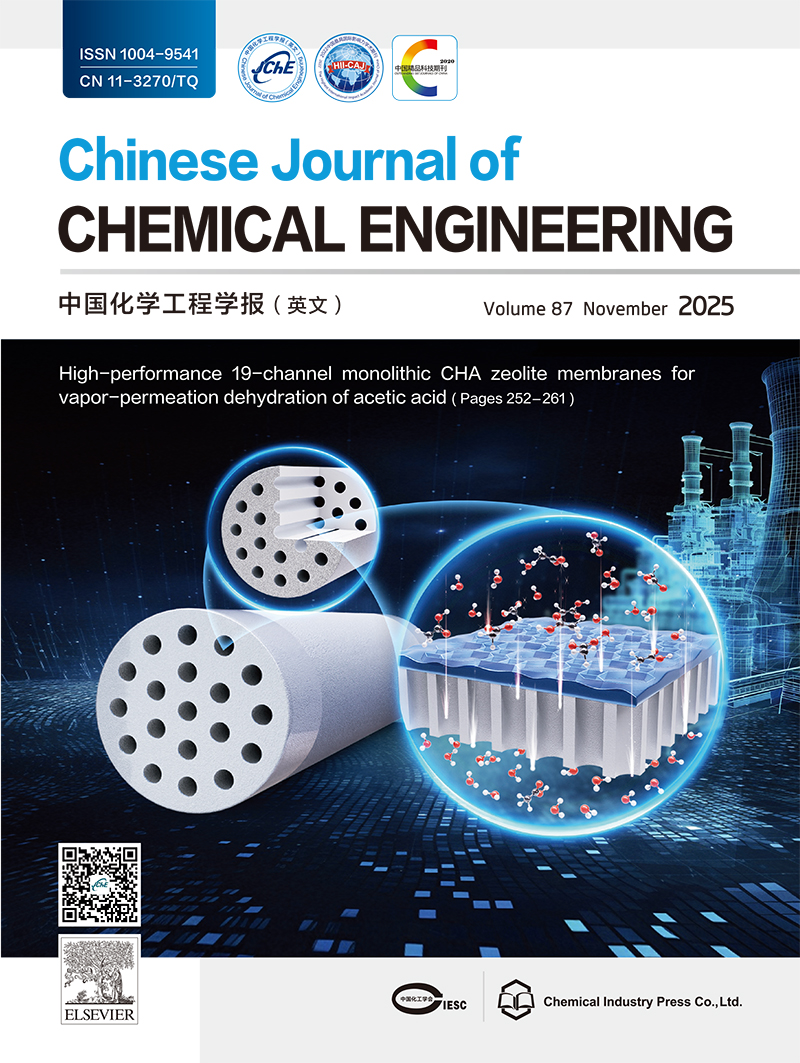
Large-area 19-channel monolithic CHA zeolite membranes enable industrial acetic acid dehydration via vapor permeation. (See Hong Xiao et al., Pages 252?261)
-
This cover illustration represents the concept of waste-to-hydrogen valorization. In the top-left, metallurgical slag waste is transformed into a multifunctional gray catalyst, shown with red -white CO2 molecules adsorbed in situ during biomass gasifi cation. In the bottom-left, wood shavings undergo catalytic gasifi cation facilitated by this material. On the right, the resulting H2-rich gas (depicted as blue pairs) highlights the overall process: metallurgical slag repurposed into a dual-function catalyst enables the conversion of wood waste into hydrogen-rich gas. The design integrates waste upcycling, catalytic transformation, and CO2 capture, conveying a dynamic and environmentally sustainable pathway. (See Zechen Zhang et al., Pages 108?123)
-
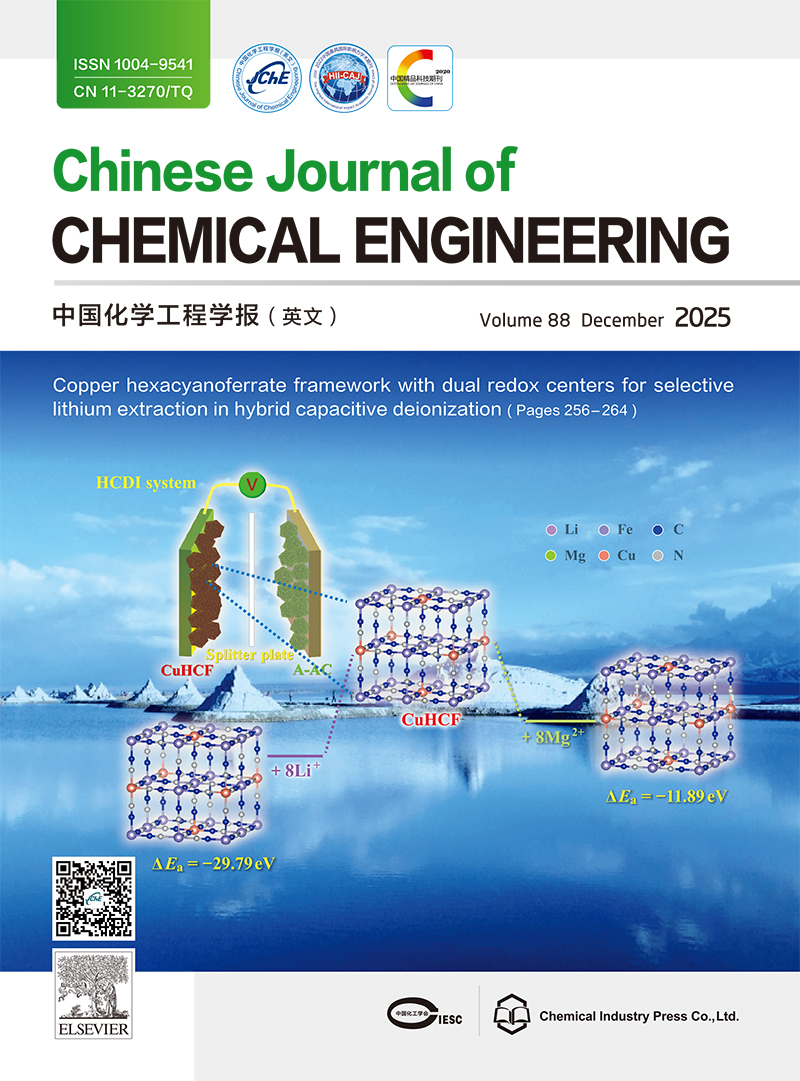
Cubic copper hexacyanoferrate (CuHCF) nanoparticles synthesized at room temperature for hybrid capacitive deionization (HCDI). CuHCF nanoparticles demonstrate high Li+ selectivity in HCDI system via dual redox- active sites ([FeIII(CN)6]4-/[FeII(CN)6]3- and Cu+/Cu2+) and ionic sieving, supported by DFT-confi rmed lower Li+ adsorption energy (-3.72 eV vs. -1.49 eV(Mg2+)), enabling effi cient lithium extraction from high-salinity resources. (See Li Zhang et al., Pages 256-264)
-
28 December 2025, Volume 88 Issue 12
-
Please wait a minute...
Permeation characteristics of light hydrocarbons through Poly(amide-6-b-ethylene oxide) multilayer composite membranes PDF (0KB) Heat Transfer Behavior in a Square Duct with Tandem Wire Coil Element Insert PDF (0KB) 基于ARX-NNPLS模型的优化策略及在聚合物牌号切换过程中的应用ARX-NNPLS PDF (0KB) 甲烷/乙烯/空气预混火焰层流燃烧速度与火焰稳定性的数值研究 PDF (0KB) Advances in LES Studies on Two-Phase Combustion--Part II: LES of Complex Engineering Gas-Particle Flows and Coal Combustion PDF (0KB) Lixing Zhou - [an error occurred while processing this directive]
- [an error occurred while processing this directive]
-
中国化学工程学报 -
» Numerical Study of Solid-Liquid Two-Phase Flow in Stirred Tanks with Rushton Impeller (I) Formulation and Simulation of Flow Field WANG Feng, WANG Weijing, MAO Zaishao . 2004 Vol. 12 (5): 599-609 Cited by: Baidu(91) » Kinetics of Non-catalyzed Decomposition of Glucose in High-temperature Liquid Water JING Qi, LÜ Xiuyang . 2008 Vol. 16 (6): 890-894 Cited by: Baidu(83) » Prediction of Flash Point Temperature of Organic Compounds Using a Hybrid Method of Group Contribution+Neural Network+Particle Swarm Optimization Juan A. Lazzús . 2010 Vol. 18 (5): 817-823 Cited by: Baidu(62) » Gas-Liquid Microreaction Technology:Recent Developments and Future Challenges CHEN Guangwen, YUE Jun, YUAN Quan Chin.J.Chem.Eng.. 2008 Vol. 16 (5): 663-669 Cited by: Baidu(59)
Journal Introduction
Started in 1982(Monthly)
Editor-in-Chief:FEI Weiyang
Executive Editor-in-Chief: LUO Guangsheng
Sponsored: Chemical Industry and Engineering Society of China,
Chemical Industry Press Co., Ltd.
ISSN: 1004-9541
CN: 11-3270/TQ
Editor-in-Chief:FEI Weiyang
Executive Editor-in-Chief: LUO Guangsheng
Sponsored: Chemical Industry and Engineering Society of China,
Chemical Industry Press Co., Ltd.
ISSN: 1004-9541
CN: 11-3270/TQ
Editorial NewsMore...
Promotion
Most DownloadMore...
InformationMore...
LinksMore...
- Chemical Industry and Engineering Society of China
- Chemical Industry Press Co., Ltd.
- China Association for Science and Technology
- Chinese Academy of Sciences
- Chinese Academy of Engineering
- OSID
- CNKI
- Wanfang Data
- Scopus
- ScienceDirect
- Clarivate Analytics
- CIESC Journal
- Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress
- Energy Storage Science and Technology

CJCHE Wechat
AdvertisementMore...









 Submit a Manuscript
Submit a Manuscript
 View All Issues
View All Issues
 Get Content Alert
Get Content Alert



 京公网安备 11010102001993号
京公网安备 11010102001993号